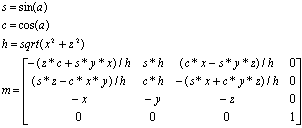
(* Note that the values (x,y,z) here are normalized inside the function)
guAlign
Creates a modeling matrix for rotation around an arbitrary axis (aligned, fixed-point)
#include <ultra64.h> /* gu.h */
void guAlign(Mtx *m, float a, float x, float y, float z);None
This macro performs an alignment process (in which the arbitrary axis represented by the line passing through the origin and a point (x, y, z) is rotated so it points in the same direction as the negative Z axis), and then returns a modeling matrix to the structure indicated by m for use in rotating by an angle of a degrees in the positive direction around this arbitrary axis. The result of calling this macro is the creation of a modeling matrix like the one shown below. Note that a unit matrix is returned when h = 0.
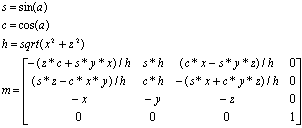
(* Note that the values (x,y,z) here are normalized inside the function)
For a detailed explanation about the fixed-point format, see gSPMatrix. Floating-point is handled using guAlignF.
The vector 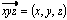 does not have to be normalized ahead of time. This is done inside the function. However, when
does not have to be normalized ahead of time. This is done inside the function. However, when
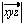 = 0 the operation of this macro cannot be guaranteed.
= 0 the operation of this macro cannot be guaranteed.
The Mtx structure is shown below:
typedef long Mtx_t[4][4];
typedef union {
Mtx_t m;
long long int force_structure_alignment;
} Mtx;
gSPMatrix, guAlignF, guRotate, guRotateF, guScale, guScaleF, guTranslate, and guTranslateF
03/01/99 Completely rewritten.