guPosition
Creates a rotation/parallel translation modeling matrix (fixed point)
#include <ultra64.h> /* gu.h */
void guPosition(
Mtx *m,
float r,
float p,
float h,
float s,
float x,
float y,
float z);None
Scales by s the object rotated according to (r, p, h) and returns the modeling matrix translated by (x, y, z) to the structure indicated by m. When this function is called, the result is the creation of the following kind of modeling matrix:
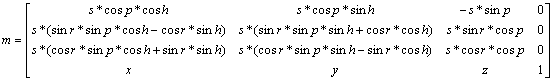
For details about the fixed-point format, see gSPMatrix. Floating point is handled with the guPositionF function.
An angle with a positive value represents counter-clockwise rotation. Be careful about the corresponding axis and the order of rotation.
The Mtx structure looks like this:
typedef long Mtx_t[4][4];
typedef union {
Mtx_t m;
long long int force_structure_alignment;
} Mtx;
gSPMatrix, guAlign, guAlignF, guPositionF, guRotate, guRotateF, guScale, guScaleF, guTranslate, and guTranslateF
03/01/99 Completely rewritten.